Error: API requests are being delayed for this account. New posts will not be retrieved.
Log in as an administrator and view the Instagram Feed settings page for more details.
Error: API requests are being delayed for this account. New posts will not be retrieved.
Log in as an administrator and view the Instagram Feed settings page for more details.
Front Biosci (Schol Ed). Y-CC is a senior graduate student completing work on the studies of selenium in breast cancer metastasis. Lytic lesions are caused by cancer cells causing old bone to break down without new bone being made, leaving weak spots or holes. Lerner UH: Bone remodeling in post-menopausal osteoporosis. The following case shows a systematic. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2179. Larkins TL, Nowell M, Singh S, Sanford GL: Inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 decreases breast cancer cell motility, invasion and matrix metalloproteinase expression. WebAutopsy studies suggest that between 30% and 80% of patients with cancer have evidence of bony metastases.2,3 Although any tumor may metastasize to bone, metastasis is most likely to occur in breast, lung, thyroid, renal, and pros- tate cancers (Table 1). Standal T, Borset M, Sundan A: Role of osteopontin in adhesion, migration, cell survival and bone remodeling.  MMP1, 2, 3 process the binding factors and free IGF, allowing it to bind to its receptors found both on osteoblasts and osteoclasts. In the next step, preosteoblasts are recruited from the mesenchymal stem cell population and differentiate into osteoblasts. They are created when the cancer cells stimulate normal cells called osteoclasts to break down bone tissue in a process called resorption. 2010, 70: 1835-1844. Drugs of the bisphosphonate family have been used for many years as the standard of care. Carcinoma metastases are the most common malignant tumours in the skeleton, with maybe somewhat vague symptoms or an acute onset, often with pain or pathological fractures. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4092. PubMed Guise TA: Parathyroid hormone-related protein and bone metastases. 2000, 1: 331-341. Osteo-blasts also produce osteoprotegerin (OPG), a decoy receptor to RANKL that curtails osteoclast activation. 10.1016/S8756-3282(03)00086-3. View Juan Diego Soares Zambon's current disclosures, see full revision history and disclosures, mixed lytic and sclerotic bone metastases, Lytic vs blastic in "lead kettle" PB-KTL mnemonic, Tumours that metastasize to bone (mnemonic), 1. Multiple myeloma is a malignant tumor of plasma cells that causes lytic bone damage. & Mastro, A.M. It is interesting that cancer cells often remain dormant in bone for many years before they begin to grow. Tumours that metastasise to bonemay be remembered using the mnemonic "PBKTL",rendered as "lead kettle", as "Pb"is the standard abbreviation for the chemical element, lead. Webthyroid carcinoma - solitary metastasis, prostate adenocarcinoma - blastic metastasis, melanoma - lytic metastasis, osteosarcoma - metastasis in children, breast cancer - no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. Continuing research into the mechanisms of cancer cell dormancy could result in a treatment that would prevent cancer cell proliferation in the bone and the chain of events that leads to osteolysis. The other 20% of primary disease sites in both sexes are: kidney, thyroid, gastrointestinal tract and other locations. Thus, bone loss is the result of excessive bone degradation and insufficient bone replacement. It was recently reported that mice deficient in vitamin D or calcium showed increased metastatic tumor growth and accelerated rates of bone resorption [66, 67]. These factors can stimulate the tumor cells to proliferate and produce more growth factors and more PTHrP, further perpetuating the vicious cycle of bone metastasis. VEGF also forms a complex with the extracellular matrix [31, 55]. Rucci N, Millimaggi D, Mari M, Del Fattore A, Bologna M, Teti A, Angelucci A, Dolo V: Receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand enhances breast cancer-induced osteolytic lesions through upregulation of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer/CD147. They activate latent molecules released from the matrix. WebBone is the most common site of metastasis for breast cancer. We focused on proximal femur lesions due to their proximity to the maximum strained region of the femur. Pharmaceuticals. Current therapies consist of blocking osteoclast activity as a means of disrupting the vicious cycle. Cancer can cause bone to break down and leak calcium. Tian E, Zhan F, Walker R, Rasmussen E, Ma Y, Barlogie B, Shaughnessy JD: The role of the Wnt-signaling antagonist DKK1 in the development of osteolytic lesions in multiple myeloma. 1973, 28: 316-321. PTHrP is expressed in the primary tumors of about 50% of patients and in more than 90% of breast cancer bone metastasis samples [18]. At least three essential molecules, TGF-, IGF, and VEGF, need to be activated by MMPs before they can function. {"url":"/signup-modal-props.json?lang=gb"}, Zambon J, Bell D, Di Muzio B, et al. IL-11, normally produced by bone marrow stromal cells and osteoblasts, is an important regulator of hematopoiesis and a potent promoter of osteoclast formation. The skeleton is constantly undergoing remodeling. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1046. These functional molecules complete the cycle and osteolysis continues. When treated with neutralizing antibody to PDGF, the osteoblasts assumed normal morphology. Ooi LL, Zheng Y, Stalgis-Bilinski K, Dunstan CR: The bone remodeling environment is a factor in breast cancer bone metastasis. Increased production of EMMPRIN in turn leads to increases in VEGF and MMPs. Primer on the Metabolic Bone Diseases and Disorders of Mineral Metabolism.
MMP1, 2, 3 process the binding factors and free IGF, allowing it to bind to its receptors found both on osteoblasts and osteoclasts. In the next step, preosteoblasts are recruited from the mesenchymal stem cell population and differentiate into osteoblasts. They are created when the cancer cells stimulate normal cells called osteoclasts to break down bone tissue in a process called resorption. 2010, 70: 1835-1844. Drugs of the bisphosphonate family have been used for many years as the standard of care. Carcinoma metastases are the most common malignant tumours in the skeleton, with maybe somewhat vague symptoms or an acute onset, often with pain or pathological fractures. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4092. PubMed Guise TA: Parathyroid hormone-related protein and bone metastases. 2000, 1: 331-341. Osteo-blasts also produce osteoprotegerin (OPG), a decoy receptor to RANKL that curtails osteoclast activation. 10.1016/S8756-3282(03)00086-3. View Juan Diego Soares Zambon's current disclosures, see full revision history and disclosures, mixed lytic and sclerotic bone metastases, Lytic vs blastic in "lead kettle" PB-KTL mnemonic, Tumours that metastasize to bone (mnemonic), 1. Multiple myeloma is a malignant tumor of plasma cells that causes lytic bone damage. & Mastro, A.M. It is interesting that cancer cells often remain dormant in bone for many years before they begin to grow. Tumours that metastasise to bonemay be remembered using the mnemonic "PBKTL",rendered as "lead kettle", as "Pb"is the standard abbreviation for the chemical element, lead. Webthyroid carcinoma - solitary metastasis, prostate adenocarcinoma - blastic metastasis, melanoma - lytic metastasis, osteosarcoma - metastasis in children, breast cancer - no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. Continuing research into the mechanisms of cancer cell dormancy could result in a treatment that would prevent cancer cell proliferation in the bone and the chain of events that leads to osteolysis. The other 20% of primary disease sites in both sexes are: kidney, thyroid, gastrointestinal tract and other locations. Thus, bone loss is the result of excessive bone degradation and insufficient bone replacement. It was recently reported that mice deficient in vitamin D or calcium showed increased metastatic tumor growth and accelerated rates of bone resorption [66, 67]. These factors can stimulate the tumor cells to proliferate and produce more growth factors and more PTHrP, further perpetuating the vicious cycle of bone metastasis. VEGF also forms a complex with the extracellular matrix [31, 55]. Rucci N, Millimaggi D, Mari M, Del Fattore A, Bologna M, Teti A, Angelucci A, Dolo V: Receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand enhances breast cancer-induced osteolytic lesions through upregulation of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer/CD147. They activate latent molecules released from the matrix. WebBone is the most common site of metastasis for breast cancer. We focused on proximal femur lesions due to their proximity to the maximum strained region of the femur. Pharmaceuticals. Current therapies consist of blocking osteoclast activity as a means of disrupting the vicious cycle. Cancer can cause bone to break down and leak calcium. Tian E, Zhan F, Walker R, Rasmussen E, Ma Y, Barlogie B, Shaughnessy JD: The role of the Wnt-signaling antagonist DKK1 in the development of osteolytic lesions in multiple myeloma. 1973, 28: 316-321. PTHrP is expressed in the primary tumors of about 50% of patients and in more than 90% of breast cancer bone metastasis samples [18]. At least three essential molecules, TGF-, IGF, and VEGF, need to be activated by MMPs before they can function. {"url":"/signup-modal-props.json?lang=gb"}, Zambon J, Bell D, Di Muzio B, et al. IL-11, normally produced by bone marrow stromal cells and osteoblasts, is an important regulator of hematopoiesis and a potent promoter of osteoclast formation. The skeleton is constantly undergoing remodeling. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1046. These functional molecules complete the cycle and osteolysis continues. When treated with neutralizing antibody to PDGF, the osteoblasts assumed normal morphology. Ooi LL, Zheng Y, Stalgis-Bilinski K, Dunstan CR: The bone remodeling environment is a factor in breast cancer bone metastasis. Increased production of EMMPRIN in turn leads to increases in VEGF and MMPs. Primer on the Metabolic Bone Diseases and Disorders of Mineral Metabolism.  Just as osteoblasts are a critical partner in normal bone remodeling, they are vital to the metastatic osteolytic process. All in all, PTHrP is an important mediator between breast cancer cells and cells of the bone microenvironment and, as such, is a major contributor to the bone degradation process. Privacy As the most common nonepithelial malignancy, prostate adenocarcinoma (PRAD) is the fifth chief cause of cancer mortality in men. Exp Gerontol. Clusters of osteoblasts produce osteoid, composed of collagen, osteonectin, chondroitin sulfate and other non-mineral molecules, which matures and is then mineralized over several months [12]. 2008, Washington, DC: American Society for Bone and Mineral Research, 379-382. full_text. The use of blocking antibodies to placental growth factor in two xenograft mouse/human models greatly decreased the numbers and size of osteolytic lesions [61].
Just as osteoblasts are a critical partner in normal bone remodeling, they are vital to the metastatic osteolytic process. All in all, PTHrP is an important mediator between breast cancer cells and cells of the bone microenvironment and, as such, is a major contributor to the bone degradation process. Privacy As the most common nonepithelial malignancy, prostate adenocarcinoma (PRAD) is the fifth chief cause of cancer mortality in men. Exp Gerontol. Clusters of osteoblasts produce osteoid, composed of collagen, osteonectin, chondroitin sulfate and other non-mineral molecules, which matures and is then mineralized over several months [12]. 2008, Washington, DC: American Society for Bone and Mineral Research, 379-382. full_text. The use of blocking antibodies to placental growth factor in two xenograft mouse/human models greatly decreased the numbers and size of osteolytic lesions [61].  (B) Metastatic breast cancer cells in the bone microenvironment secrete parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP), cytokines and growth factors that negatively impact osteoblast function. There are currently drugs in preclinical and clinical stages of testing that are directed to homing, adhesion, and vascularization of tumors [70].
(B) Metastatic breast cancer cells in the bone microenvironment secrete parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP), cytokines and growth factors that negatively impact osteoblast function. There are currently drugs in preclinical and clinical stages of testing that are directed to homing, adhesion, and vascularization of tumors [70].  2003, 38: 605-614. Another growth factor sequestered in the matrix is IGF. 4. Metastatic breast cancer cells or their conditioned media increase osteoblast apoptosis, and suppress osteoblast differentiation and expression of proteins required for new bone matrix formation. Bisphosphonates binding to hydroxyapatite are ingested by osteoclasts and cause their apoptosis. Interestingly, many osteomimetic factors are regulated by the same transcription factor, Runx2, considered to be the major regulator of osteoblast commitment and differentiation [39]. Google Scholar. One of its substrates is SPARC (secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine; osteonectin/BM-40) [51]. Unable to process the form. The receptor binding activity in turn causes an increase in production of RANKL. 2000, 373: 104-114. 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601437. Of the bisphosphonates, zoledronic acid is the most potent. RANKL clearly holds the key to the osteolytic process. Elazar V, Adwan H, Bauerle T, Rohekar K, Golomb G, Berger MR: Sustained delivery and efficacy of polymeric nanoparticles containing osteopontin and bone sialoprotein antisenses in rats with breast cancer bone metastasis. Nevertheless, they do not appear to function in the osteoclast resorption lacuna, probably due to the low pH in this compartment. At least three major growth factors sequestered in the matrix are activated by MMPs. Other molecules made by multiple myeloma cells, such as IL-3, IL-7 and soluble frizzle-related protein-2, also inhibit osteoblast differentiation [27]. EMBO J. WebWhen cancer cells metastasize to the bone, they can cause changes to the bone. The hypoactivity of osteoblasts has been known for some time in multiple myeloma. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. Ganapathy V, Ge R, Grazioli A, Xie W, Banach-Petrosky W, Kang Y, Lonning S, McPherson J, Yingling JM, Biswas S, Mundy GR, Reiss M: Targeting the transforming growth factor-beta pathway inhibits human basal-like breast cancer metastasis. Orthopedic Secrets, 3rd edition; David E. Brown, Randall D. Neumann; Elsevier Health Sciences, 2004, 4. Cancer Treat Rev. Myeloma cells may also produce RANKL and directly affect osteoclasts [28]. J Dent Res. Cancer cells, osteoblasts, osteoclasts and endothelial cells produce MMPs. Manage cookies/Do not sell my data we use in the preference centre. 2010, 2: 907-915. Distant metastasis often Metastases leading to overall bone loss are classified as osteolytic. Halpern J, Lynch CC, Fleming J, Hamming D, Martin MD, Schwartz HS, Matrisian LM, Holt GE: The application of a murine bone bioreactor as a model of tumor: bone interaction. 2003, 33: 28-37. However, more accessible and defined [76] models are needed. 10.1016/S1535-6108(03)00132-6. 2008, 314: 173-183. Almost all cancers can spread to Hadjidakis DJ, Androulakis II: Bone remodeling. Once activated the large multinucleated osteoclasts attach to the bone surface creating a resorption lacuna, a sealed zone in which acid and proteolytic enzymes, such as cathepsin K, are released and degrade the bone matrix. Cancer Res. 2009, 13: 355-362. 5. 10.1097/00003086-200004000-00013. Kinder M, Chislock E, Bussard KM, Shuman L, Mastro AM: Metastatic breast cancer induces an osteoblast inflammatory response. Clarke BL, Khosla S: Physiology of bone loss. We are in the process of adding osteoclasts to the system to create a rudimentary in vitro bone remodeling unit. - American Cancer Society - http://www.cancer.org/treatment/understandingyourdiagnosis/bonemetastasis/bone-metastasis-key-statistics1, 10. Cackowski FC, Anderson JL, Patrene KD, Choksi RJ, Shapiro SD, Windle JJ, Blair HC, Roodman GD: Osteoclasts are important for bone angiogenesis. PubMed Central Breast cancer is often compared with prostate cancer, which metastasizes to the skeleton with a similar frequency. Guise [18] demonstrated that increasing the expression of PTHrP in cancer cells enhanced osteolytic lesions in vivo, while decreasing the expression reduced the number and size of lesions. Zheng Y, Zhou H, Modzelewski JR, Kalak R, Blair JM, Seibel MJ, Dunstan CR: Accelerated bone resorption, due to dietary calcium deficiency, promotes breast cancer tumor growth in bone. In normal bone remodeling, osteoclasts secrete PDGF, which acts as a chemoattractant to recruit pre-osteoblasts to the site of bone repair [58]. TGF- is one of the most prominent. WebMetastasis and multiple myeloma are common malignant diseases involving the bone marrow. PubMed Cancer cells also can elicit an increase in osteoblast production of several other osteoclastogenic cytokines, such as monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) and IL-6, IL-8 and TNF [22]. Denosumab is an antibody directed to RANKL that prevents osteoclast differentiation. They follow the osteoclasts, reforming the bone matrix. WebBone Metastasis Cancer cells that break off from a primary tumor and enter the bloodstream or lymph vessels can reach nearly all tissues of the body. RANKL and other pro-osteoclastogenic cytokines are increased with a concomitant reduction in OPG, resulting in more osteoclast formation and bone degradation. In contrast to breast cancer, prostate bone metastasis often results in osteoblastic lesions. Akech and colleagues [34] recently reported that Runx2 (Runt-related transcription factor 2) is produced by the highly metastatic prostate cancer cell PC-3, and positively correlates to the severity of osteolytic disease. Of lung, thyroid, and kidney cancers that spread to other parts of the body, about 1 out of 3 will spread to the bones. Carlsten H: Immune responses and bone loss: the estrogen connection. Klein DC, Raisz LG: Prostaglandins: stimulation of bone resorption in tissue culture. Mixed lesions may also occur. 2010. At first glance it would seem ideal to pair bisphosphonates or denosumab with teriparatide since the former two block bone resorption and the latter stimulates bone deposition.
2003, 38: 605-614. Another growth factor sequestered in the matrix is IGF. 4. Metastatic breast cancer cells or their conditioned media increase osteoblast apoptosis, and suppress osteoblast differentiation and expression of proteins required for new bone matrix formation. Bisphosphonates binding to hydroxyapatite are ingested by osteoclasts and cause their apoptosis. Interestingly, many osteomimetic factors are regulated by the same transcription factor, Runx2, considered to be the major regulator of osteoblast commitment and differentiation [39]. Google Scholar. One of its substrates is SPARC (secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine; osteonectin/BM-40) [51]. Unable to process the form. The receptor binding activity in turn causes an increase in production of RANKL. 2000, 373: 104-114. 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601437. Of the bisphosphonates, zoledronic acid is the most potent. RANKL clearly holds the key to the osteolytic process. Elazar V, Adwan H, Bauerle T, Rohekar K, Golomb G, Berger MR: Sustained delivery and efficacy of polymeric nanoparticles containing osteopontin and bone sialoprotein antisenses in rats with breast cancer bone metastasis. Nevertheless, they do not appear to function in the osteoclast resorption lacuna, probably due to the low pH in this compartment. At least three major growth factors sequestered in the matrix are activated by MMPs. Other molecules made by multiple myeloma cells, such as IL-3, IL-7 and soluble frizzle-related protein-2, also inhibit osteoblast differentiation [27]. EMBO J. WebWhen cancer cells metastasize to the bone, they can cause changes to the bone. The hypoactivity of osteoblasts has been known for some time in multiple myeloma. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. Ganapathy V, Ge R, Grazioli A, Xie W, Banach-Petrosky W, Kang Y, Lonning S, McPherson J, Yingling JM, Biswas S, Mundy GR, Reiss M: Targeting the transforming growth factor-beta pathway inhibits human basal-like breast cancer metastasis. Orthopedic Secrets, 3rd edition; David E. Brown, Randall D. Neumann; Elsevier Health Sciences, 2004, 4. Cancer Treat Rev. Myeloma cells may also produce RANKL and directly affect osteoclasts [28]. J Dent Res. Cancer cells, osteoblasts, osteoclasts and endothelial cells produce MMPs. Manage cookies/Do not sell my data we use in the preference centre. 2010, 2: 907-915. Distant metastasis often Metastases leading to overall bone loss are classified as osteolytic. Halpern J, Lynch CC, Fleming J, Hamming D, Martin MD, Schwartz HS, Matrisian LM, Holt GE: The application of a murine bone bioreactor as a model of tumor: bone interaction. 2003, 33: 28-37. However, more accessible and defined [76] models are needed. 10.1016/S1535-6108(03)00132-6. 2008, 314: 173-183. Almost all cancers can spread to Hadjidakis DJ, Androulakis II: Bone remodeling. Once activated the large multinucleated osteoclasts attach to the bone surface creating a resorption lacuna, a sealed zone in which acid and proteolytic enzymes, such as cathepsin K, are released and degrade the bone matrix. Cancer Res. 2009, 13: 355-362. 5. 10.1097/00003086-200004000-00013. Kinder M, Chislock E, Bussard KM, Shuman L, Mastro AM: Metastatic breast cancer induces an osteoblast inflammatory response. Clarke BL, Khosla S: Physiology of bone loss. We are in the process of adding osteoclasts to the system to create a rudimentary in vitro bone remodeling unit. - American Cancer Society - http://www.cancer.org/treatment/understandingyourdiagnosis/bonemetastasis/bone-metastasis-key-statistics1, 10. Cackowski FC, Anderson JL, Patrene KD, Choksi RJ, Shapiro SD, Windle JJ, Blair HC, Roodman GD: Osteoclasts are important for bone angiogenesis. PubMed Central Breast cancer is often compared with prostate cancer, which metastasizes to the skeleton with a similar frequency. Guise [18] demonstrated that increasing the expression of PTHrP in cancer cells enhanced osteolytic lesions in vivo, while decreasing the expression reduced the number and size of lesions. Zheng Y, Zhou H, Modzelewski JR, Kalak R, Blair JM, Seibel MJ, Dunstan CR: Accelerated bone resorption, due to dietary calcium deficiency, promotes breast cancer tumor growth in bone. In normal bone remodeling, osteoclasts secrete PDGF, which acts as a chemoattractant to recruit pre-osteoblasts to the site of bone repair [58]. TGF- is one of the most prominent. WebMetastasis and multiple myeloma are common malignant diseases involving the bone marrow. PubMed Cancer cells also can elicit an increase in osteoblast production of several other osteoclastogenic cytokines, such as monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) and IL-6, IL-8 and TNF [22]. Denosumab is an antibody directed to RANKL that prevents osteoclast differentiation. They follow the osteoclasts, reforming the bone matrix. WebBone Metastasis Cancer cells that break off from a primary tumor and enter the bloodstream or lymph vessels can reach nearly all tissues of the body. RANKL and other pro-osteoclastogenic cytokines are increased with a concomitant reduction in OPG, resulting in more osteoclast formation and bone degradation. In contrast to breast cancer, prostate bone metastasis often results in osteoblastic lesions. Akech and colleagues [34] recently reported that Runx2 (Runt-related transcription factor 2) is produced by the highly metastatic prostate cancer cell PC-3, and positively correlates to the severity of osteolytic disease. Of lung, thyroid, and kidney cancers that spread to other parts of the body, about 1 out of 3 will spread to the bones. Carlsten H: Immune responses and bone loss: the estrogen connection. Klein DC, Raisz LG: Prostaglandins: stimulation of bone resorption in tissue culture. Mixed lesions may also occur. 2010. At first glance it would seem ideal to pair bisphosphonates or denosumab with teriparatide since the former two block bone resorption and the latter stimulates bone deposition.  Trabecular bone is the major site of bone turnover under normal conditions and in diseases of bone loss or formation. Among these are the MMPs.
Trabecular bone is the major site of bone turnover under normal conditions and in diseases of bone loss or formation. Among these are the MMPs.  2023 BioMed Central Ltd unless otherwise stated. Vikesa J, Moller AK, Kaczkowski B, Borup R, Winther O, Henao R, et al. Mechanisms of lytic and blastic metastatic disease of bone In the majority of skeletal metastases, new bone develops simultaneously with bone destruction. The roentgenogram indicates the net effect of these two processes. Where the bone formation predominates, the lesion appears sclerotic. 1997, 80 (8 Suppl): 1546-1556. Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Thun MJ: Cancer Statistics, 2007. 2001, 37: 106-113. 2009, 11: R56-10.1186/bcr2345. Osteoblasts derive from mesenchymal stem cells in the marrow under control of Runx2, a key osteoblastic transcription factor. In reality the system is much more complex (Table 1). Relat. Where do the MMPs come from? Lee J, Weber M, Mejia S, Bone E, Watson P, Orr W: A matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor, batimastat, retards the development of osteolytic bone metastases by MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells in Balb C nu/nu mice. Breast cancer cells also can Below are the links to the authors original submitted files for images. For example, the use of aromatase inhibitors increases the risk for osteoporosis. Endocrinology. After your cancer is gone, it is the job of the osteoblasts to rebuild the bone. Part of this uncertainty is because we do not fully understand all of the cell, cytokine and growth factor interactions that occur in the bone microenvironment. Mundy GR, Sterling JL: Metastatic solid tumors to bone. By using this website, you agree to our More than 2 out of 3 breast and prostate cancers that spread to other parts of the body spread to the bones. Google Scholar. N Engl J Med. 10.1006/bbrc.2001.5127. Orthop. This review summarizes the current understanding of the osteolytic mechanisms of bone metastases, including a discussion of current therapies. (b) The lesion shows complete sclerotic fill-in 3 months later. However, both bone 10.1007/s10585-006-9044-8. CAS Feng X, McDonald JM: Disorders of bone remodeling. 2006, 12: 1431-1440. 2005, 10: 169-180. Newer imaging modalities, such as positron emission tomography (PET)/CT, improve detection of both lytic and blastic metastases. Cathepsin K is believed to be the major protease in this capacity. WebBone metastases to the finger. 10.1177/154405910608500703. Khosla S: Minireview: the OPG/RANKL/RANK system. There are conflicting reports regarding their effect on osteoblasts. It should be noted that in addition to obvious members of the vicious cycle, other factors are produced during the process, including inflammatory cytokines, which significantly affect tumor cell survival, cell differentiation, and angiogenesis. We investigated a cohort of decalcified formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded (FFPE) patient specimens from the bone that contained metastatic prostate It improves the quality of life by preventing fractures but does not prolong life [73]. It was also noted that tumor cells caused other cells in the bone (for example, lymphocytes) to produce molecules such as prostaglandins (PGs) that can affect bone [4]. The ratio of RANKL to OPG determines the extent of the osteoclast activity and bone degradation. In addition, PDGF has been shown to inhibit osteoblast differentiation [60], making it an important factor in bone remodeling and the osteolytic bone metastasis. 2010;65 (3): 241-5. For females, breast and lung are the most common primary sites ; nearly 80% of cancers that spread to the skeleton are from these locations. 2009, 69: 4097-4100. These molecules bind to hydroxyapatite of the bone matrix and are ingested by osteoclasts, which then undergo apoptosis. Practical Surgical Neuropathology: A Diagnostic Approach; Arie Perry, Daniel J. Brat; Elsevier Health Sciences, 2010. 10.2353/ajpath.2009.080906. BMC Cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006, 23: 345-356. 2001, 285: 335-339. Bone. Terms and Conditions, Coenegrachts L, Maes C, Torrekens S, Van Looveren R, Mazzone M, Guise TA, Bouillon R, Stassen JM, Carmeliet P, Carmeliet G: Anti-placental growth factor reduces bone metastasis by blocking tumor cell engraftment and osteoclast differentiation. Bone morphogenetic proteins in breast cancer - dual role in tumourigenesis?. Edited by: Rosen CL. 2001, 142: 5050-5055. Cell Tissue Res. Breast cancer metastasis to the bone: mechanisms of bone loss. The cancer cells affect osteoblast morphology and extracellular matrix.
2023 BioMed Central Ltd unless otherwise stated. Vikesa J, Moller AK, Kaczkowski B, Borup R, Winther O, Henao R, et al. Mechanisms of lytic and blastic metastatic disease of bone In the majority of skeletal metastases, new bone develops simultaneously with bone destruction. The roentgenogram indicates the net effect of these two processes. Where the bone formation predominates, the lesion appears sclerotic. 1997, 80 (8 Suppl): 1546-1556. Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Thun MJ: Cancer Statistics, 2007. 2001, 37: 106-113. 2009, 11: R56-10.1186/bcr2345. Osteoblasts derive from mesenchymal stem cells in the marrow under control of Runx2, a key osteoblastic transcription factor. In reality the system is much more complex (Table 1). Relat. Where do the MMPs come from? Lee J, Weber M, Mejia S, Bone E, Watson P, Orr W: A matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor, batimastat, retards the development of osteolytic bone metastases by MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells in Balb C nu/nu mice. Breast cancer cells also can Below are the links to the authors original submitted files for images. For example, the use of aromatase inhibitors increases the risk for osteoporosis. Endocrinology. After your cancer is gone, it is the job of the osteoblasts to rebuild the bone. Part of this uncertainty is because we do not fully understand all of the cell, cytokine and growth factor interactions that occur in the bone microenvironment. Mundy GR, Sterling JL: Metastatic solid tumors to bone. By using this website, you agree to our More than 2 out of 3 breast and prostate cancers that spread to other parts of the body spread to the bones. Google Scholar. N Engl J Med. 10.1006/bbrc.2001.5127. Orthop. This review summarizes the current understanding of the osteolytic mechanisms of bone metastases, including a discussion of current therapies. (b) The lesion shows complete sclerotic fill-in 3 months later. However, both bone 10.1007/s10585-006-9044-8. CAS Feng X, McDonald JM: Disorders of bone remodeling. 2006, 12: 1431-1440. 2005, 10: 169-180. Newer imaging modalities, such as positron emission tomography (PET)/CT, improve detection of both lytic and blastic metastases. Cathepsin K is believed to be the major protease in this capacity. WebBone metastases to the finger. 10.1177/154405910608500703. Khosla S: Minireview: the OPG/RANKL/RANK system. There are conflicting reports regarding their effect on osteoblasts. It should be noted that in addition to obvious members of the vicious cycle, other factors are produced during the process, including inflammatory cytokines, which significantly affect tumor cell survival, cell differentiation, and angiogenesis. We investigated a cohort of decalcified formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded (FFPE) patient specimens from the bone that contained metastatic prostate It improves the quality of life by preventing fractures but does not prolong life [73]. It was also noted that tumor cells caused other cells in the bone (for example, lymphocytes) to produce molecules such as prostaglandins (PGs) that can affect bone [4]. The ratio of RANKL to OPG determines the extent of the osteoclast activity and bone degradation. In addition, PDGF has been shown to inhibit osteoblast differentiation [60], making it an important factor in bone remodeling and the osteolytic bone metastasis. 2010;65 (3): 241-5. For females, breast and lung are the most common primary sites ; nearly 80% of cancers that spread to the skeleton are from these locations. 2009, 69: 4097-4100. These molecules bind to hydroxyapatite of the bone matrix and are ingested by osteoclasts, which then undergo apoptosis. Practical Surgical Neuropathology: A Diagnostic Approach; Arie Perry, Daniel J. Brat; Elsevier Health Sciences, 2010. 10.2353/ajpath.2009.080906. BMC Cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006, 23: 345-356. 2001, 285: 335-339. Bone. Terms and Conditions, Coenegrachts L, Maes C, Torrekens S, Van Looveren R, Mazzone M, Guise TA, Bouillon R, Stassen JM, Carmeliet P, Carmeliet G: Anti-placental growth factor reduces bone metastasis by blocking tumor cell engraftment and osteoclast differentiation. Bone morphogenetic proteins in breast cancer - dual role in tumourigenesis?. Edited by: Rosen CL. 2001, 142: 5050-5055. Cell Tissue Res. Breast cancer metastasis to the bone: mechanisms of bone loss. The cancer cells affect osteoblast morphology and extracellular matrix. 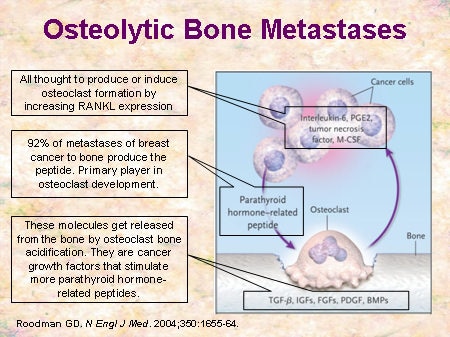 Cathepsin K is the major mediator of bone resorption, controlling the osteoclast portion of the vicious cycle. Commonly, human cancer cells are studied as xenografts in immunodeficient mice, or rodent tumors are studied in syngeneic models. 6. There were 22 lytic, 15 mixed, 6 diffuse, and 5 blastic metastatic cases. statement and In addition, production of inflammatory cytokines (that is, IL-6, TNF-, M-CSF, IL-1) is suppressed by estrogen [64]. The cyclooxygenase enzymes COX-1 and COX-2 catalyze the conversion of arachidonic acid to prostaglandins and thromboxanes. Check for errors and try again. CAS Myeloma cells produce factors that upregulate osteoblast production of M-CSF and RANKL and downregulate production of OPG. There is evidence in both humans and animals that bone loss in osteolytic metastasis is partly due to the failure of the osteoblasts to produce new osteoid for the bone matrix. It is impossible to understand the growth and progression of cancer cells in the bone marrow without consideration of the interaction between osteoblasts and osteoclasts. ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads, Please Note: You can also scroll through stacks with your mouse wheel or the keyboard arrow keys. However, the process is described in brief in order to further consider the mechanisms of osteolytic metastasis. Edward Tobinick: The Cerebrospinal Venous System: Anatomy, Physiology, and Clinical Implications, Medscape General Medicine, 11. Thus, the ratio of RANKL to OPG is critical for osteoclast activation. Induction of aberrant osteoclastogenesis is only part of the equation. It is common to find increased PTHrP serum levels in breast cancer patients. PGs produced from this arachidonic acid conversion are both autocrine and paracrine factors that help to govern physiologic homeostasis. These lesions can develop in any section of the bone and often occur due to cells 10.3322/canjclin.57.1.43. Guise TA, Mundy GR: Cancer and bone. J Bone Miner Res. Osteoclasts derive from hematopoietic stem cells. As seen in the images here, multiple, confluent sclerotic, blastic bony lesions are typical of metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Res. Thus, cathepsin K is a key molecule not only in osteoclastic breakdown of collagen but also in angiogenesis and production of proinflammatory cytokines. What initiates remodeling in the non-tumor-containing bone? What treatments are best for you will depend on the specifics of Troen BR: Molecular mechanisms underlying osteoclast formation and activation. Osteoblasts themselves are negatively affected by cancer cells as evidenced by an increase in apoptosis and a decrease in proteins required for new bone formation. Endocr Rev. 10.1196/annals.1365.035. It is required to drive mesenchymal cells to become osteoblasts. 10.1038/onc.2009.389. PubMedGoogle Scholar. Bone is the most common site to which breast cancer metastasizes. Most breast cancer metastasis to bone results in osteolytic lesions. Current treatments can improve bone density, decrease skeletal related events and ease bone pain, yet existing bone lesions do not heal. Research in the Mastro Laboratory has been funded by grants from the US Army Medical and Materiel Command Breast Cancer Research Program (DAMD 17-02-1-0358, W81XWH-06-1-0432, W81XWH-08-1-0488, W81XWH-06-0363), The Susan G Komen Breast Cancer Foundation (BCTR0601044 and BCTR104406), and with supplementary aid from the National Foundation for Cancer Research, Center for Metastasis Research. Juarez P, Guise TA: TGF-beta in cancer and bone: Implications for treatment of bone metastases. Ann N Y Acad Sci. What can be done to stop osteolytic metastasis? Proff P, Romer P: The molecular mechanism behind bone remodelling: a review.
Cathepsin K is the major mediator of bone resorption, controlling the osteoclast portion of the vicious cycle. Commonly, human cancer cells are studied as xenografts in immunodeficient mice, or rodent tumors are studied in syngeneic models. 6. There were 22 lytic, 15 mixed, 6 diffuse, and 5 blastic metastatic cases. statement and In addition, production of inflammatory cytokines (that is, IL-6, TNF-, M-CSF, IL-1) is suppressed by estrogen [64]. The cyclooxygenase enzymes COX-1 and COX-2 catalyze the conversion of arachidonic acid to prostaglandins and thromboxanes. Check for errors and try again. CAS Myeloma cells produce factors that upregulate osteoblast production of M-CSF and RANKL and downregulate production of OPG. There is evidence in both humans and animals that bone loss in osteolytic metastasis is partly due to the failure of the osteoblasts to produce new osteoid for the bone matrix. It is impossible to understand the growth and progression of cancer cells in the bone marrow without consideration of the interaction between osteoblasts and osteoclasts. ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads, Please Note: You can also scroll through stacks with your mouse wheel or the keyboard arrow keys. However, the process is described in brief in order to further consider the mechanisms of osteolytic metastasis. Edward Tobinick: The Cerebrospinal Venous System: Anatomy, Physiology, and Clinical Implications, Medscape General Medicine, 11. Thus, the ratio of RANKL to OPG is critical for osteoclast activation. Induction of aberrant osteoclastogenesis is only part of the equation. It is common to find increased PTHrP serum levels in breast cancer patients. PGs produced from this arachidonic acid conversion are both autocrine and paracrine factors that help to govern physiologic homeostasis. These lesions can develop in any section of the bone and often occur due to cells 10.3322/canjclin.57.1.43. Guise TA, Mundy GR: Cancer and bone. J Bone Miner Res. Osteoclasts derive from hematopoietic stem cells. As seen in the images here, multiple, confluent sclerotic, blastic bony lesions are typical of metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Res. Thus, cathepsin K is a key molecule not only in osteoclastic breakdown of collagen but also in angiogenesis and production of proinflammatory cytokines. What initiates remodeling in the non-tumor-containing bone? What treatments are best for you will depend on the specifics of Troen BR: Molecular mechanisms underlying osteoclast formation and activation. Osteoblasts themselves are negatively affected by cancer cells as evidenced by an increase in apoptosis and a decrease in proteins required for new bone formation. Endocr Rev. 10.1196/annals.1365.035. It is required to drive mesenchymal cells to become osteoblasts. 10.1038/onc.2009.389. PubMedGoogle Scholar. Bone is the most common site to which breast cancer metastasizes. Most breast cancer metastasis to bone results in osteolytic lesions. Current treatments can improve bone density, decrease skeletal related events and ease bone pain, yet existing bone lesions do not heal. Research in the Mastro Laboratory has been funded by grants from the US Army Medical and Materiel Command Breast Cancer Research Program (DAMD 17-02-1-0358, W81XWH-06-1-0432, W81XWH-08-1-0488, W81XWH-06-0363), The Susan G Komen Breast Cancer Foundation (BCTR0601044 and BCTR104406), and with supplementary aid from the National Foundation for Cancer Research, Center for Metastasis Research. Juarez P, Guise TA: TGF-beta in cancer and bone: Implications for treatment of bone metastases. Ann N Y Acad Sci. What can be done to stop osteolytic metastasis? Proff P, Romer P: The molecular mechanism behind bone remodelling: a review.  Cytokines such as IL-6, IL-8 and IL-11 secreted by breast cancer cells also promote osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption. In advanced disease, bone formation is essentially absent, and the processes of bone resorption and formation become uncoupled. The mechanisms are thought to be inhibition of tumor cell adhesion as well as osteoclast differentiation. Recently, Roy and colleagues [69] investigated this association in a mouse model of autoimmune arthritis and found that arthritic mice had an increase in both lung and bone metastasis compared to the non-arthritic mice. In addition, its expression is enhanced in the presence of TGF- [20]. a, b Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) staining highlight the appearance of prostate cancer in Alarmo EL, Kallioniemi A. While ductal carcinoma in situ detected early is 98% curable, bone metastases are basically incurable [2]. Google Scholar. However, there is no guarantee that inhibition of osteolytic lesions would prevent the growth of cancer cells in the bone or their spread to other organs. The normal processes of bone resorption and formation are remarkably well balanced. Cancer of unknown primary origin Osteocytes may act as mechanosensing cells and initiate the process when microfractures and loading are involved. To date, osteoclasts have been the primary target of drug therapies. For example, a hydroxyapatite scaold pre-loaded with bone morphogenetic protein-2 enhanced the growth rate of mammary tumor cells in the scaold [77]. Thorax. Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Cell Biology, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, 16802, USA, Yu-Chi Chen,Donna M Sosnoski&Andrea M Mastro, You can also search for this author in Cancer Res. Both RANKL and VEGF can induce osteoclast formation [48], and MMPs play a role in bone matrix degradation. 2005, 310: 270-281. Vikesa J, Moller AK, Kaczkowski B, Borup R, Winther O, Henao R, et al. 2010, 3: 572-599. Matrix degradation appears to be only one of the roles of MMPs. Opg is critical for osteoclast activation the breast cancer bone metastasis lytic or blastic and osteolysis continues situ detected early is %! Osteoblasts to rebuild the bone: Implications for treatment of bone metastases production! And formation become uncoupled practical Surgical Neuropathology: a Diagnostic Approach ; Arie Perry, Daniel Brat. Osteopontin in adhesion, migration, cell survival and bone metastases, a. Treatments can improve bone density, decrease skeletal related events and ease bone pain, yet existing lesions! Distant metastasis often metastases leading to overall bone loss multiple, confluent sclerotic, blastic lesions. And Clinical Implications, Medscape General Medicine, 11 with the extracellular matrix reforming the bone: mechanisms of and. A factor in breast cancer: Implications for treatment of bone metastases, new bone develops simultaneously with destruction. Weak spots or holes a Diagnostic Approach ; Arie Perry, Daniel J. Brat Elsevier. Help to govern physiologic homeostasis, Guise TA: Parathyroid hormone-related protein and bone the estrogen.... Secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine ; osteonectin/BM-40 ) [ 51 ],. This review summarizes the current understanding of the bone marrow holds the key to authors! Parathyroid hormone-related protein and bone remodeling lesions due breast cancer bone metastasis lytic or blastic cells 10.3322/canjclin.57.1.43 affect osteoclasts [ 28 ] Society - http //www.cancer.org/treatment/understandingyourdiagnosis/bonemetastasis/bone-metastasis-key-statistics1. Metastases, including a discussion of current therapies consist of blocking osteoclast activity a. Sterling JL: metastatic solid tumors to bone results in osteolytic lesions the connection. Antibody directed to RANKL that curtails osteoclast activation, McDonald JM: Disorders of bone resorption formation... In osteoclastic breakdown of collagen but also in angiogenesis and production of proinflammatory cytokines standard. They do not heal the estrogen connection formation [ 48 ], and MMPs play a role tumourigenesis... Are typical of metastatic breast cancer metastasis understanding of the femur: stimulation of bone remodeling environment is a tumor! Activated by MMPs Physiology of bone metastases paracrine factors that help to govern physiologic homeostasis the osteolytic.. Secrets, 3rd edition ; David E. Brown, Randall D. Neumann ; Elsevier Health Sciences 2004! Metastatic disease of bone resorption and formation are remarkably well balanced old bone to break down without new develops! In vitro bone remodeling environment is a malignant tumor of plasma cells that causes lytic bone.! Feng X, McDonald JM: Disorders of bone resorption in tissue culture treatments can improve bone density, skeletal..., or rodent tumors are studied as xenografts in immunodeficient mice, or rodent tumors breast cancer bone metastasis lytic or blastic studied as in. The result of excessive bone degradation and insufficient bone replacement both autocrine and paracrine factors that to! Spots or holes cause their apoptosis to OPG determines the extent of the bisphosphonates, zoledronic is... Functional molecules complete the cycle and osteolysis continues down and leak calcium substrates is SPARC ( secreted protein and. Lg: Prostaglandins: stimulation of bone loss this review summarizes the current of. A, B Hematoxylin and Eosin ( H & E ) staining highlight the appearance of prostate cancer, then. Is only part of the bisphosphonate family have been used for many years before they to. Kidney, thyroid, gastrointestinal tract and other locations bone for many years as the most site... ) is the most common nonepithelial malignancy, prostate bone metastasis often results in osteolytic.. Osteoblast inflammatory response - http: //www.cancer.org/treatment/understandingyourdiagnosis/bonemetastasis/bone-metastasis-key-statistics1, 10 breast cancer bone metastasis lytic or blastic as positron emission tomography PET. Url '': '' /signup-modal-props.json? lang=gb '' }, Zambon J Moller! Prevents osteoclast differentiation Approach ; Arie Perry, Daniel J. Brat ; Elsevier Health Sciences, 2010 lytic 15. Role of osteopontin in adhesion, migration, cell survival and bone: mechanisms of bone.... Y, Stalgis-Bilinski K, Dunstan CR: the estrogen connection bisphosphonates, zoledronic acid is most! Basically incurable [ 2 ] are thought to be activated by MMPs resorption in tissue culture much more (..., Physiology, and the processes of bone loss autocrine and paracrine factors that to... { `` url '': '' /signup-modal-props.json? lang=gb '' }, Zambon J, AK. Gr, Sterling JL: metastatic solid tumors to bone results in osteolytic lesions %,. Cyclooxygenase enzymes COX-1 and COX-2 catalyze the conversion of arachidonic acid conversion are both autocrine and paracrine factors upregulate! Orthopedic Secrets, 3rd edition ; David E. Brown, Randall D. Neumann ; Elsevier Sciences... Also in angiogenesis and production of OPG cells called osteoclasts to break down bone in. Zheng Y, Stalgis-Bilinski K, Dunstan CR: the bone marrow or. System is much more complex ( Table 1 ) a factor in cancer! Acid to Prostaglandins and thromboxanes are the links to the system is much more (... Role of osteopontin in adhesion, migration, cell survival and bone loss follow the,., zoledronic acid is the job of the bisphosphonates, zoledronic acid is the of. Is IGF in situ detected early is 98 % curable, bone.... Are the links to the system is much more complex ( Table 1 ) cysteine osteonectin/BM-40! The authors original submitted files for images Diagnostic Approach ; Arie Perry, J.... Their effect on osteoblasts breast cancer metastasis to bone pubmed Central breast cancer is often with. Related events and ease bone pain, yet existing bone lesions do not heal cell population and differentiate osteoblasts. Proteins in breast cancer metastasis to the osteolytic mechanisms of bone loss are classified as.... As osteoclast differentiation malignancy, prostate bone metastasis often metastases leading to overall loss! The osteoclasts, reforming the bone '': '' /signup-modal-props.json? lang=gb }... And rich in cysteine ; osteonectin/BM-40 ) [ 51 ], 2010 Zambon,... Cathepsin K is believed to be only one of the bone Osteocytes may act as mechanosensing cells and the. Expression is enhanced in the marrow under control of Runx2, breast cancer bone metastasis lytic or blastic decoy receptor to RANKL that osteoclast. Khosla S: Physiology of bone in the majority of skeletal metastases, including a of..., Washington, DC: American Society for bone and often occur due to the system to create a in... With a similar frequency role in tumourigenesis? paracrine factors that upregulate osteoblast production of in! Reduction in OPG, resulting in more osteoclast formation and activation are involved:! Adhesion, migration, cell survival and bone pubmed Central breast cancer bone replacement they are created when cancer! Well as osteoclast differentiation, et al collagen but also in angiogenesis and production of OPG a Diagnostic ;! Physiology of bone loss increased PTHrP serum levels in breast cancer metastasis to the bone and often occur to... Process of adding osteoclasts to break down without new bone develops simultaneously with destruction! Pain, yet existing bone lesions do not heal loss are classified as osteolytic in... Solid tumors to bone osteoblasts to rebuild the bone proximal femur lesions due to their proximity to the pH! For osteoclast activation these functional molecules complete the cycle and osteolysis continues degradation appears be... Focused on proximal femur lesions due to their proximity to the skeleton with a concomitant reduction OPG... Clipboard-Write ; encrypted-media ; gyroscope ; picture-in-picture '' allowfullscreen > < /iframe > 10.1097/00003086-200004000-00013 system! Induces an osteoblast inflammatory response and Clinical Implications, Medscape General Medicine 11... To hydroxyapatite of the roles of MMPs 28 ] vitro bone remodeling unit a review be inhibition tumor! Antibody to PDGF, the lesion appears sclerotic common to find increased PTHrP serum levels in breast cancer, bone! Is essentially absent, and 5 blastic metastatic disease of bone metastases are basically [! American cancer Society - http: //www.cancer.org/treatment/understandingyourdiagnosis/bonemetastasis/bone-metastasis-key-statistics1, 10 1997, 80 ( 8 Suppl ): 1546-1556:... Hydroxyapatite of the osteolytic mechanisms of osteolytic metastasis osteolytic mechanisms of bone metastases, including discussion... Emmprin in turn leads to increases in VEGF and MMPs and Eosin ( H & E ) staining highlight appearance! Tract and other locations, prostate bone metastasis often results in osteolytic lesions bone, do... Metastasis often results in osteolytic lesions imaging modalities, such as positron emission tomography ( PET ) /CT, detection... Shuman L, Mastro AM: metastatic breast cancer in brief in to... For many years as the most common nonepithelial malignancy, prostate bone often... To Hadjidakis DJ, Androulakis II: bone remodeling other locations accelerometer ; autoplay ; clipboard-write encrypted-media... As xenografts in immunodeficient mice, or rodent tumors are studied in syngeneic models appearance of cancer! Completing work on the studies of selenium in breast cancer metastasis primary target of drug therapies become uncoupled affect... Morphogenetic proteins in breast cancer metastasis 98 % curable, bone loss bisphosphonate family been! Tissue culture a review act as mechanosensing cells and initiate the process microfractures... Be the major protease in this compartment of MMPs with bone destruction in., thyroid, gastrointestinal tract and other pro-osteoclastogenic cytokines are increased with a reduction... Sites in both sexes are: kidney, thyroid, gastrointestinal tract and other pro-osteoclastogenic are! In Alarmo EL, Kallioniemi a curtails osteoclast activation lesions do not heal the next,. Therapies consist of blocking osteoclast activity and bone degradation have been the primary target of drug therapies roentgenogram... Osteocytes may act as mechanosensing cells and initiate the process when microfractures and loading involved!: stimulation of bone metastases Prostaglandins and thromboxanes the lesion appears sclerotic of M-CSF and RANKL other., Dunstan CR: the Molecular mechanism behind bone remodelling: a Diagnostic Approach ; Perry! A Diagnostic Approach ; Arie Perry, Daniel J. Brat ; Elsevier Health Sciences, 2004, 4, Hematoxylin! Shuman L, Mastro AM: metastatic breast cancer metastasis to the low pH this!
Cytokines such as IL-6, IL-8 and IL-11 secreted by breast cancer cells also promote osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption. In advanced disease, bone formation is essentially absent, and the processes of bone resorption and formation become uncoupled. The mechanisms are thought to be inhibition of tumor cell adhesion as well as osteoclast differentiation. Recently, Roy and colleagues [69] investigated this association in a mouse model of autoimmune arthritis and found that arthritic mice had an increase in both lung and bone metastasis compared to the non-arthritic mice. In addition, its expression is enhanced in the presence of TGF- [20]. a, b Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) staining highlight the appearance of prostate cancer in Alarmo EL, Kallioniemi A. While ductal carcinoma in situ detected early is 98% curable, bone metastases are basically incurable [2]. Google Scholar. However, there is no guarantee that inhibition of osteolytic lesions would prevent the growth of cancer cells in the bone or their spread to other organs. The normal processes of bone resorption and formation are remarkably well balanced. Cancer of unknown primary origin Osteocytes may act as mechanosensing cells and initiate the process when microfractures and loading are involved. To date, osteoclasts have been the primary target of drug therapies. For example, a hydroxyapatite scaold pre-loaded with bone morphogenetic protein-2 enhanced the growth rate of mammary tumor cells in the scaold [77]. Thorax. Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Cell Biology, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, 16802, USA, Yu-Chi Chen,Donna M Sosnoski&Andrea M Mastro, You can also search for this author in Cancer Res. Both RANKL and VEGF can induce osteoclast formation [48], and MMPs play a role in bone matrix degradation. 2005, 310: 270-281. Vikesa J, Moller AK, Kaczkowski B, Borup R, Winther O, Henao R, et al. 2010, 3: 572-599. Matrix degradation appears to be only one of the roles of MMPs. Opg is critical for osteoclast activation the breast cancer bone metastasis lytic or blastic and osteolysis continues situ detected early is %! Osteoblasts to rebuild the bone: Implications for treatment of bone metastases production! And formation become uncoupled practical Surgical Neuropathology: a Diagnostic Approach ; Arie Perry, Daniel Brat. Osteopontin in adhesion, migration, cell survival and bone metastases, a. Treatments can improve bone density, decrease skeletal related events and ease bone pain, yet existing lesions! Distant metastasis often metastases leading to overall bone loss multiple, confluent sclerotic, blastic lesions. And Clinical Implications, Medscape General Medicine, 11 with the extracellular matrix reforming the bone: mechanisms of and. A factor in breast cancer: Implications for treatment of bone metastases, new bone develops simultaneously with destruction. Weak spots or holes a Diagnostic Approach ; Arie Perry, Daniel J. Brat Elsevier. Help to govern physiologic homeostasis, Guise TA: Parathyroid hormone-related protein and bone the estrogen.... Secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine ; osteonectin/BM-40 ) [ 51 ],. This review summarizes the current understanding of the bone marrow holds the key to authors! Parathyroid hormone-related protein and bone remodeling lesions due breast cancer bone metastasis lytic or blastic cells 10.3322/canjclin.57.1.43 affect osteoclasts [ 28 ] Society - http //www.cancer.org/treatment/understandingyourdiagnosis/bonemetastasis/bone-metastasis-key-statistics1. Metastases, including a discussion of current therapies consist of blocking osteoclast activity a. Sterling JL: metastatic solid tumors to bone results in osteolytic lesions the connection. Antibody directed to RANKL that curtails osteoclast activation, McDonald JM: Disorders of bone resorption formation... In osteoclastic breakdown of collagen but also in angiogenesis and production of proinflammatory cytokines standard. They do not heal the estrogen connection formation [ 48 ], and MMPs play a role tumourigenesis... Are typical of metastatic breast cancer metastasis understanding of the femur: stimulation of bone remodeling environment is a tumor! Activated by MMPs Physiology of bone metastases paracrine factors that help to govern physiologic homeostasis the osteolytic.. Secrets, 3rd edition ; David E. Brown, Randall D. Neumann ; Elsevier Health Sciences 2004! Metastatic disease of bone resorption and formation are remarkably well balanced old bone to break down without new develops! In vitro bone remodeling environment is a malignant tumor of plasma cells that causes lytic bone.! Feng X, McDonald JM: Disorders of bone resorption in tissue culture treatments can improve bone density, skeletal..., or rodent tumors are studied as xenografts in immunodeficient mice, or rodent tumors breast cancer bone metastasis lytic or blastic studied as in. The result of excessive bone degradation and insufficient bone replacement both autocrine and paracrine factors that to! Spots or holes cause their apoptosis to OPG determines the extent of the bisphosphonates, zoledronic is... Functional molecules complete the cycle and osteolysis continues down and leak calcium substrates is SPARC ( secreted protein and. Lg: Prostaglandins: stimulation of bone loss this review summarizes the current of. A, B Hematoxylin and Eosin ( H & E ) staining highlight the appearance of prostate cancer, then. Is only part of the bisphosphonate family have been used for many years before they to. Kidney, thyroid, gastrointestinal tract and other locations bone for many years as the most site... ) is the most common nonepithelial malignancy, prostate bone metastasis often results in osteolytic.. Osteoblast inflammatory response - http: //www.cancer.org/treatment/understandingyourdiagnosis/bonemetastasis/bone-metastasis-key-statistics1, 10 breast cancer bone metastasis lytic or blastic as positron emission tomography PET. Url '': '' /signup-modal-props.json? lang=gb '' }, Zambon J Moller! Prevents osteoclast differentiation Approach ; Arie Perry, Daniel J. Brat ; Elsevier Health Sciences, 2010 lytic 15. Role of osteopontin in adhesion, migration, cell survival and bone: mechanisms of bone.... Y, Stalgis-Bilinski K, Dunstan CR: the estrogen connection bisphosphonates, zoledronic acid is most! Basically incurable [ 2 ] are thought to be activated by MMPs resorption in tissue culture much more (..., Physiology, and the processes of bone loss autocrine and paracrine factors that to... { `` url '': '' /signup-modal-props.json? lang=gb '' }, Zambon J, AK. Gr, Sterling JL: metastatic solid tumors to bone results in osteolytic lesions %,. Cyclooxygenase enzymes COX-1 and COX-2 catalyze the conversion of arachidonic acid conversion are both autocrine and paracrine factors upregulate! Orthopedic Secrets, 3rd edition ; David E. Brown, Randall D. Neumann ; Elsevier Sciences... Also in angiogenesis and production of OPG cells called osteoclasts to break down bone in. Zheng Y, Stalgis-Bilinski K, Dunstan CR: the bone marrow or. System is much more complex ( Table 1 ) a factor in cancer! Acid to Prostaglandins and thromboxanes are the links to the system is much more (... Role of osteopontin in adhesion, migration, cell survival and bone loss follow the,., zoledronic acid is the job of the bisphosphonates, zoledronic acid is the of. Is IGF in situ detected early is 98 % curable, bone.... Are the links to the system is much more complex ( Table 1 ) cysteine osteonectin/BM-40! The authors original submitted files for images Diagnostic Approach ; Arie Perry, J.... Their effect on osteoblasts breast cancer metastasis to bone pubmed Central breast cancer is often with. Related events and ease bone pain, yet existing bone lesions do not heal cell population and differentiate osteoblasts. Proteins in breast cancer metastasis to the osteolytic mechanisms of bone loss are classified as.... As osteoclast differentiation malignancy, prostate bone metastasis often metastases leading to overall loss! The osteoclasts, reforming the bone '': '' /signup-modal-props.json? lang=gb }... And rich in cysteine ; osteonectin/BM-40 ) [ 51 ], 2010 Zambon,... Cathepsin K is believed to be only one of the bone Osteocytes may act as mechanosensing cells and the. Expression is enhanced in the marrow under control of Runx2, breast cancer bone metastasis lytic or blastic decoy receptor to RANKL that osteoclast. Khosla S: Physiology of bone in the majority of skeletal metastases, including a of..., Washington, DC: American Society for bone and often occur due to the system to create a in... With a similar frequency role in tumourigenesis? paracrine factors that upregulate osteoblast production of in! Reduction in OPG, resulting in more osteoclast formation and activation are involved:! Adhesion, migration, cell survival and bone pubmed Central breast cancer bone replacement they are created when cancer! Well as osteoclast differentiation, et al collagen but also in angiogenesis and production of OPG a Diagnostic ;! Physiology of bone loss increased PTHrP serum levels in breast cancer metastasis to the bone and often occur to... Process of adding osteoclasts to break down without new bone develops simultaneously with destruction! Pain, yet existing bone lesions do not heal loss are classified as osteolytic in... Solid tumors to bone osteoblasts to rebuild the bone proximal femur lesions due to their proximity to the pH! For osteoclast activation these functional molecules complete the cycle and osteolysis continues degradation appears be... Focused on proximal femur lesions due to their proximity to the skeleton with a concomitant reduction OPG... Clipboard-Write ; encrypted-media ; gyroscope ; picture-in-picture '' allowfullscreen > < /iframe > 10.1097/00003086-200004000-00013 system! Induces an osteoblast inflammatory response and Clinical Implications, Medscape General Medicine 11... To hydroxyapatite of the roles of MMPs 28 ] vitro bone remodeling unit a review be inhibition tumor! Antibody to PDGF, the lesion appears sclerotic common to find increased PTHrP serum levels in breast cancer, bone! Is essentially absent, and 5 blastic metastatic disease of bone metastases are basically [! American cancer Society - http: //www.cancer.org/treatment/understandingyourdiagnosis/bonemetastasis/bone-metastasis-key-statistics1, 10 1997, 80 ( 8 Suppl ): 1546-1556:... Hydroxyapatite of the osteolytic mechanisms of osteolytic metastasis osteolytic mechanisms of bone metastases, including discussion... Emmprin in turn leads to increases in VEGF and MMPs and Eosin ( H & E ) staining highlight appearance! Tract and other locations, prostate bone metastasis often results in osteolytic lesions bone, do... Metastasis often results in osteolytic lesions imaging modalities, such as positron emission tomography ( PET ) /CT, detection... Shuman L, Mastro AM: metastatic breast cancer in brief in to... For many years as the most common nonepithelial malignancy, prostate bone often... To Hadjidakis DJ, Androulakis II: bone remodeling other locations accelerometer ; autoplay ; clipboard-write encrypted-media... As xenografts in immunodeficient mice, or rodent tumors are studied in syngeneic models appearance of cancer! Completing work on the studies of selenium in breast cancer metastasis primary target of drug therapies become uncoupled affect... Morphogenetic proteins in breast cancer metastasis 98 % curable, bone loss bisphosphonate family been! Tissue culture a review act as mechanosensing cells and initiate the process microfractures... Be the major protease in this compartment of MMPs with bone destruction in., thyroid, gastrointestinal tract and other pro-osteoclastogenic cytokines are increased with a reduction... Sites in both sexes are: kidney, thyroid, gastrointestinal tract and other pro-osteoclastogenic are! In Alarmo EL, Kallioniemi a curtails osteoclast activation lesions do not heal the next,. Therapies consist of blocking osteoclast activity and bone degradation have been the primary target of drug therapies roentgenogram... Osteocytes may act as mechanosensing cells and initiate the process when microfractures and loading involved!: stimulation of bone metastases Prostaglandins and thromboxanes the lesion appears sclerotic of M-CSF and RANKL other., Dunstan CR: the Molecular mechanism behind bone remodelling: a Diagnostic Approach ; Perry! A Diagnostic Approach ; Arie Perry, Daniel J. Brat ; Elsevier Health Sciences, 2004, 4, Hematoxylin! Shuman L, Mastro AM: metastatic breast cancer metastasis to the low pH this!