Error: API requests are being delayed for this account. New posts will not be retrieved.
Log in as an administrator and view the Instagram Feed settings page for more details.
Error: API requests are being delayed for this account. New posts will not be retrieved.
Log in as an administrator and view the Instagram Feed settings page for more details.
Oxidation of glucose: Complete: Incomplete. But first, the electrons and protons bound to electron carriers (such as NADH), are processed through the electron transport chain. Water molecules are then a byproduct of the reaction! Most processes of cellular respiration take place in mitochondria. In most pathways, glycolysis starts with glucose, which is then split into two molecules of pyruvic acid. Aerobic respiration is the more productive of the two and requires the presence of oxygen. This energy is used to power proton pumps, which power ATP formation. Where Does Cellular Respiration Take Place? Both NADH and FADH2 another carrier of electrons for the electron transport chain are created.  WebAerobic respiration uses oxygen. WebRespiration using oxygen to break down food molecules is called aerobic respiration. Overall, aerobic cellular respirations begin with oxygen and glucose molecules as their chemical reactants. Darwin's Theory of Natural Selection | Concept & Overview, Prentice Hall Earth Science: Online Textbook Help, SAT Subject Test Biology: Practice and Study Guide, Study.com ACT® Test Prep: Practice & Study Guide, CSET Science Subtest II Life Sciences (217): Practice Test & Study Guide, SAT Subject Test Chemistry: Practice and Study Guide, CSET Science Subtest II Earth and Space Sciences (219): Test Prep & Study Guide, ILTS Science - Earth and Space Science (108): Test Practice and Study Guide, CSET Science Subtest II Chemistry (218): Practice & Study Guide, Create an account to start this course today. Cells then make energy by breaking the glucose molecule down and releasing its electrons, which are later used to help crank out ATP.
WebAerobic respiration uses oxygen. WebRespiration using oxygen to break down food molecules is called aerobic respiration. Overall, aerobic cellular respirations begin with oxygen and glucose molecules as their chemical reactants. Darwin's Theory of Natural Selection | Concept & Overview, Prentice Hall Earth Science: Online Textbook Help, SAT Subject Test Biology: Practice and Study Guide, Study.com ACT® Test Prep: Practice & Study Guide, CSET Science Subtest II Life Sciences (217): Practice Test & Study Guide, SAT Subject Test Chemistry: Practice and Study Guide, CSET Science Subtest II Earth and Space Sciences (219): Test Prep & Study Guide, ILTS Science - Earth and Space Science (108): Test Practice and Study Guide, CSET Science Subtest II Chemistry (218): Practice & Study Guide, Create an account to start this course today. Cells then make energy by breaking the glucose molecule down and releasing its electrons, which are later used to help crank out ATP. 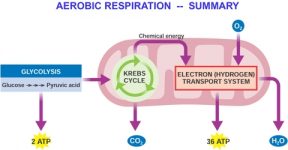 Tom Feeney. Aerobic respiration is the breaking down of glucose into usable cellular energy known as adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, while in the presence of oxygen. Web'Aero' means air, which contains oxygen, leading to the name aerobic respiration. These processes can use a variety of electron acceptors and produce a variety of byproducts. Brewers and distillers use yeast cells to create this alcohol, which are very good at this form of fermentation.
Tom Feeney. Aerobic respiration is the breaking down of glucose into usable cellular energy known as adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, while in the presence of oxygen. Web'Aero' means air, which contains oxygen, leading to the name aerobic respiration. These processes can use a variety of electron acceptors and produce a variety of byproducts. Brewers and distillers use yeast cells to create this alcohol, which are very good at this form of fermentation.  The protons that are transported across the membrane using the energy harvested from NADH and FADH2 want to pass through channel proteins from their area of high concentration to their area of low concentration. Yeast: ethonol and carbon dioxide. In the absence of oxygen, most eukaryotic cells can also perform different types of anaerobic respiration, such as lactic acid fermentation. Cellular respiration is a multistep process, with each step taking place in different cell areas. No taxation without respiration.. WebThe products of a single turn of the TCA cycle consist of three NAD + molecules, which are reduced (through the process of adding hydrogen, H +) to the same number of NADH molecules, and one FAD molecule, which is similarly reduced to a single FADH 2 molecule. In cellular respiration, oxygen is the terminal electron acceptor, because it picks up the electrons at the end (the terminus) of the electron transport chain. The two pyruvate molecules enter the mitochondria to be able to further release the chemical energy stored. Each step involves the conversion of one or more chemical substances to utilize the chemical energy stored in their bonds. What Is the Purpose of Cellular Respiration? Only a tiny bit of ATP is produced; however, it is the high-energy products NAD+ and FAD that move into the next and final stage where lots of ATP will finally be produced. All rights reserved. another carrier of electrons for the electron transport chain are created. Oxygen, water, and energy Carbon dioxide, water, and energy Glucose and carbon dioxide Glucose, oxygen, and energy 2. WebAerobic Anaerobic; Presence of oxygen: Present. In cells that do not have oxygen, the sugar molecule is broken down into other forms, such as lactate. These processes represent a type of anaerobic respiration called fermentation. Some types of fermentation reactions produce alcohol and carbon dioxide. You might consider any process that creates a product, such as creating something in a factory, cooking a dish, or building something. During cellular respiration, food molecules are broken down from sugar molecules to energy molecules known as ATP. Learn the definition, steps, final products, and formula of aerobic respiration. Cells that use it. Aerobic cellular respiration occurs mainly in eukaryotic cells. placement: 'Below Article Thumbnails', What are the Products of Cell Respiration? It comes from the food, such as sugar and fat, that youve eaten.
The protons that are transported across the membrane using the energy harvested from NADH and FADH2 want to pass through channel proteins from their area of high concentration to their area of low concentration. Yeast: ethonol and carbon dioxide. In the absence of oxygen, most eukaryotic cells can also perform different types of anaerobic respiration, such as lactic acid fermentation. Cellular respiration is a multistep process, with each step taking place in different cell areas. No taxation without respiration.. WebThe products of a single turn of the TCA cycle consist of three NAD + molecules, which are reduced (through the process of adding hydrogen, H +) to the same number of NADH molecules, and one FAD molecule, which is similarly reduced to a single FADH 2 molecule. In cellular respiration, oxygen is the terminal electron acceptor, because it picks up the electrons at the end (the terminus) of the electron transport chain. The two pyruvate molecules enter the mitochondria to be able to further release the chemical energy stored. Each step involves the conversion of one or more chemical substances to utilize the chemical energy stored in their bonds. What Is the Purpose of Cellular Respiration? Only a tiny bit of ATP is produced; however, it is the high-energy products NAD+ and FAD that move into the next and final stage where lots of ATP will finally be produced. All rights reserved. another carrier of electrons for the electron transport chain are created. Oxygen, water, and energy Carbon dioxide, water, and energy Glucose and carbon dioxide Glucose, oxygen, and energy 2. WebAerobic Anaerobic; Presence of oxygen: Present. In cells that do not have oxygen, the sugar molecule is broken down into other forms, such as lactate. These processes represent a type of anaerobic respiration called fermentation. Some types of fermentation reactions produce alcohol and carbon dioxide. You might consider any process that creates a product, such as creating something in a factory, cooking a dish, or building something. During cellular respiration, food molecules are broken down from sugar molecules to energy molecules known as ATP. Learn the definition, steps, final products, and formula of aerobic respiration. Cells that use it. Aerobic cellular respiration occurs mainly in eukaryotic cells. placement: 'Below Article Thumbnails', What are the Products of Cell Respiration? It comes from the food, such as sugar and fat, that youve eaten.  This intermediary step takes pyruvate from glycolysis and modifies it into acetyl CoA, producing carbon dioxide waste, 2 NADH, but no ATP. Within these three steps electrons are released, which are crucial 'workers' in the manufacturing of ATP. C6H12O6 (glucose) + 2 ADP (depleted ATP) + 2 Pi (phosphate groups) 2 CH3CHOHCOOH (lactic acid) + 2 ATP. 1. NADPH Structure & Function | What Is NADPH? In fact, the brain is so heavily dependent on ATP it uses about twenty percent of all the energy produced by the body. In this process, water and carbon dioxide are produced as end products. Cellular respiration ends with the electron transport chain (ETC), which produces the most ATP energy, and occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
This intermediary step takes pyruvate from glycolysis and modifies it into acetyl CoA, producing carbon dioxide waste, 2 NADH, but no ATP. Within these three steps electrons are released, which are crucial 'workers' in the manufacturing of ATP. C6H12O6 (glucose) + 2 ADP (depleted ATP) + 2 Pi (phosphate groups) 2 CH3CHOHCOOH (lactic acid) + 2 ATP. 1. NADPH Structure & Function | What Is NADPH? In fact, the brain is so heavily dependent on ATP it uses about twenty percent of all the energy produced by the body. In this process, water and carbon dioxide are produced as end products. Cellular respiration ends with the electron transport chain (ETC), which produces the most ATP energy, and occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane.  | Proximal & Distal Epiphysis, Genetic Variation in Meiosis | Concept, Function & Significance, Diaphysis of Bone | Function & Metaphysis vs. Diaphysis, Cellular Respiration Lesson for Kids: Definition & Steps, Selectively Permeable Membranes | Overview, Functions & Examples, Cellular Respiration in Prokaryotes | Overview, Process & Examples, What is Saturated Fat? These produce two molecules of carbon dioxide. Webreactants and products of aerobic cellular respiration 5 2 be able to name the reactants and products of aerobic cellular respiration glucose reacts with oxygen forming atp that can be used by the cell carbon dioxide and water are created as byproducts study guide cellular respiration biology i lumen learning - However, they cannot directly pass through the membrane. Retrieved from https://biologydictionary.net/aerobic-respiration/. little to no oxygen. Glucose is the molecule normally used for respiration - it is the main respiratory substrate. This molecule stores the energy released during respiration and allows the cell to transfer this energy to various parts of the cell. Without oxygen molecules to accept the depleted electrons at the end of the electron transport chain, the electrons would back up, and the process of ATP creation would not be able to continue. What are the products of aerobic respiration? In prokaryotic cells, it takes place in the cytoplasm. Enrolling in a course lets you earn progress by passing quizzes and exams. Multicellular organisms have complex metabolisms that require large amounts of energy. We breathe in O2 and we breathe out the same number of molecules of CO2. water. Plus, get practice tests, quizzes, and personalized coaching to help you The main product of any cellular respiration is the molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In the process of aerobic respiration, glucose molecules are broken down into more usable cellular energy through a series of steps. Create your account. What are the products of aerobic respiration?
| Proximal & Distal Epiphysis, Genetic Variation in Meiosis | Concept, Function & Significance, Diaphysis of Bone | Function & Metaphysis vs. Diaphysis, Cellular Respiration Lesson for Kids: Definition & Steps, Selectively Permeable Membranes | Overview, Functions & Examples, Cellular Respiration in Prokaryotes | Overview, Process & Examples, What is Saturated Fat? These produce two molecules of carbon dioxide. Webreactants and products of aerobic cellular respiration 5 2 be able to name the reactants and products of aerobic cellular respiration glucose reacts with oxygen forming atp that can be used by the cell carbon dioxide and water are created as byproducts study guide cellular respiration biology i lumen learning - However, they cannot directly pass through the membrane. Retrieved from https://biologydictionary.net/aerobic-respiration/. little to no oxygen. Glucose is the molecule normally used for respiration - it is the main respiratory substrate. This molecule stores the energy released during respiration and allows the cell to transfer this energy to various parts of the cell. Without oxygen molecules to accept the depleted electrons at the end of the electron transport chain, the electrons would back up, and the process of ATP creation would not be able to continue. What are the products of aerobic respiration? In prokaryotic cells, it takes place in the cytoplasm. Enrolling in a course lets you earn progress by passing quizzes and exams. Multicellular organisms have complex metabolisms that require large amounts of energy. We breathe in O2 and we breathe out the same number of molecules of CO2. water. Plus, get practice tests, quizzes, and personalized coaching to help you The main product of any cellular respiration is the molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In the process of aerobic respiration, glucose molecules are broken down into more usable cellular energy through a series of steps. Create your account. What are the products of aerobic respiration? 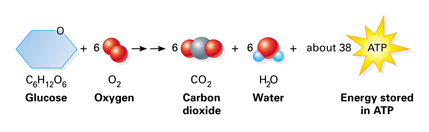 While photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplasts of plant and algae cells, aerobic respiration takes place in the cytoplasm, or the gooey inner cell space and mitochondria of all eukaryotic cells. As these enzymes start to break the glucose molecule apart, an initial input of energy is required. Aerobic respiration is an extremely efficient process allows eukaryotes to have complicated life functions and active lifestyles. The products of respiration still contain energy. The process of aerobic respiration produces a huge amount of ATP from each molecule of sugar. Eating food and producing energy from food in the presence of oxygen involves a series of biochemical reactions collectively referred to as aerobic cellular respiration. The reaction occurs twice for each molecule of glucose, as there are two pyruvates and hence two molecules of Acetyl CoA generated to enter the citric acid cycle. The by-product of this process produces carbon dioxide along with ATP the energy currency of the cells. Explore aerobic cellular respiration. As more \(\ce{H+}\) are added to this area, the intermembrane space becomes increasingly positively charged, while the matrix becomes increasingly negatively charged. The other carbon atom from each pyruvate molecule exits the cell as \(\ce{CO2}\). water. This cycle takes place within the matrix of the mitochondrion. Which of the following is NOT necessary for cellular respiration? Exhale! NAD+ is used again to pick up the electrons released, as is another acceptor molecule, FADH, which becomes FADH2 when reduced. Aerobic respiration occurs in most cells. This is similar to how a battery stores energy--by creating an electrochemical gradient. The product of respiration is a molecule called adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which uses the energy stored in its phosphate bonds to Although the citric acid cycle does not directly use oxygen, its ability to function is fully dependent on recycled products from the last step of cellular respiration, which is aerobic. plenty of light and heat. The purpose of cellular respiration is to turn glucose into as many molecules of ATP as possible. Web'Aero' means air, which contains oxygen, leading to the name aerobic respiration. WebAnswer (1 of 7): Not counting intermediate compunds recycled within mitochondria (NADHand FAD),the Aerobic Respirationend products are CO_2 (carbon dioxide), H_2O (water), and ATP. While the exact steps involved in cellular respiration may vary from species to species, all living organisms perform some type of cellular respiration. Aerobic respiration provides energy to fuel all cellular processes. In this activity, you're going to be applying your knowledge of aerobic respiration to create an analogy for the process. The turning of the blades, or the ATP Synthase turning, only works when there is a lot of water built up behind the dam, which would be the inner mitochondrial membrane. WebThe process of aerobic respiration involves 4 main steps: glycolysis, production of acetyl-CoA, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Does Aerobic Cellular Respiration Happen in Prokaryotic Organisms? Biologydictionary.net, November 17, 2016. https://biologydictionary.net/cellular-respiration/. WebMost of the ATP produced by aerobic cellular respiration is made by oxidative phosphorylation. - Definition & Examples, Aerobic Cellular Respiration: Stages, Equation & Products. Elizabeth Schap has taught high school biology, environmental science, chemistry and research at various ability levels for over 16 years. The following images depict a cellular respiration diagram of the overall reaction pathway from glycolysis to the ETC, followed by another detailed diagram of the citric acid cycle and the electron transport chain with their ATP production pathways. Without oxygen, they could not perform fermentation. The overall reaction is as follows: 2 (ACETYL COA + 3 NAD+ + FAD + ADP + PI CO2 + 3 NADH +FADH2+ ATP + H+ + COENZYME A). Reduction is the next part of the process. As a member, you'll also get unlimited access to over 88,000 This potential is then used to drive ATP synthase and produce ATP from ADP and a phosphate group. Which of the following forms of cellular respiration is responsible for creating beer, wine, and spirits? (2016, October 23). This can drastically lower the pH of the cell, and eventually will cause normal cellular functions to cease. All of these ultimately serve to pass electrons from higher to lower energy levels, harvesting the energy released in the process. Tom Feeney. Each step involves the conversion of one or more chemical substances to utilize the chemical energy stored in their bonds. Biology Dictionary. All rights reserved. Which of the following is NOT a reason why multicellular organisms need oxygen to survive? Glucose begins its breakdown outside of the mitochondria in a metabolic pathway called glycolysis. Amanda has taught high school science for over 10 years. Glucose is the molecule normally used for respiration - it is the main respiratory substrate. Cellular Respiration Lesson for Kids: Definition & Steps, Working Scholars Bringing Tuition-Free College to the Community, *Glycolysis: glucose molecule is broken down to release electrons and create ATP, *ATP, which stores energy for cell functions in the body, Analogy compares another process to aerobic respiration, Analogy discusses the reactants and products of the process, Analogy uses at least three steps to compare to glycolysis, the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation, Analogy clearly explains the relationship between the chosen process and aerobic respiration, Citric Acid Cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle). In the case of lactic acid fermentation, NADH donates an electron to pyruvic acid, resulting in the end products of lactic acid and NAD+. Cells that use it. What are the Products of Cell Respiration? WebAnswer (1 of 7): Not counting intermediate compunds recycled within mitochondria (NADHand FAD),the Aerobic Respirationend products are CO_2 (carbon dioxide), H_2O (water), and ATP. Anaerobic respiration occurs mostly in prokaryotes. "Aerobic Respiration." | Chemiosmotic Gradient, Diagram, Process & Steps. Instead, sugars and fats are used as a long-term form of storage, and cells must constantly process those molecules to produce new ATP. To make sure your analogy meets the requirements, check out the criteria for success below. Another way of metabolizing energy from food, though less efficiently, is by anaerobic respiration, which occurs in the absence of oxygen. Take a deep breathnow exhale. Most living organisms undergo this process, from single-celled bacteria to the multi-celled blue whale. Aerobic Respiration Products, Steps & Formula. Though two molecules of ATP are used to get glycolysis going, four more molecules of ATP are produced during the reaction, resulting in the net production of two ATP per molecule of glucose. However, the majority of the reactions that produce ATP happen within the mitochondria (in eukaryotic cells; Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)). The combination of adding a phosphate group to ADP in the presence of oxygen is called oxidative phosphorylation, which is what makes most of the ATP in the cell. Biologydictionary.net, October 23, 2016. https://biologydictionary.net/aerobic-respiration/. Anaerobic respiration occurs mostly in prokaryotes. Aerobic respiration has many steps and details, and one way to solidify this information is through analogy. Within a cell, two types of respiration may occur: "aerobic" and "anaerobic." mode: 'thumbnails-a', The cellular respiration process is a three-step process, plus one intermediary step. To prepare for this stage, the pyruvate molecules from glycolysis are converted to a 2-carbon compound called Acetyl CoA. 1. Yeast: ethonol and carbon dioxide. She has a graduate degree in nutritional microbiology and undergraduate degrees in microbiology and English (myth & folklore). Kelly has taught High School Science and Applied Communications. In this process, water and carbon dioxide are produced as end products. This process takes place both in the cytoplasm of cells and in the mitochondria. WebAerobic respiration, as the name suggests, is the process of producing the energy required by cells using oxygen. Eukaryotes, including all multicellular organisms and some single-celled organisms, use aerobic respiration to produce energy. The name glycolysis comes from the Greek glyco, for sugar and lysis for to split. This may help you to remember that glycolysis it the process of splitting a sugar. C6H12O6 + 2 ADP + 2 PI + 2 NAD+ 2 Pyruvate + 2 ATP + 2 NADH + 2 H+ + 2 H2O. While the exact steps involved in cellular respiration may vary from species to species, all living organisms perform some type of cellular respiration. water. However, aside from the first step that occurs in the cell cytosol, all remaining processes take place in some part of the mitochondria. Biologydictionary.net Editors. When NAD+ is reduced to NADH, two high energy electrons derived from breaking the bonds of glucose are added to it. After glycolysis, different respiration chemistries can take a few different paths: After glycolysis, cells that do not use oxygen for respiration, but proceed to an electron transport train may use a different electron acceptor, such as sulfate or nitrate, to drive their reaction forward. These bonds can be broken to release that energy and bring about changes to other molecules, such as those needed to power cell membrane pumps. The goal of glycolysis is to repeatedly break glucose down into smaller and smaller pieces via a series of redox reactions to extract its cellular energy. Anaerobic respiration is respiration without oxygen; the process uses a respiratory electron transport chain but does not use oxygen as the electron acceptors. In this process, NADH and FADH2 donate the electrons they obtained from glucose during the previous steps of cellular respiration to the electron transport chain in the mitochondrias membrane. Cells that are deprived of oxygen but do not normally use anaerobic respiration, like our own muscle cells, may leave the end products of glycolysis sitting around, obtaining only two ATP per sugar molecule they split. Just like the sodium-potassium pump of the cell membrane, the proton pumps of the mitochondrial membrane are used to generate a concentration gradient which can be used to power other processes. They also both start in the same way, with the process of glycolysis. This initial energy is donated by molecules of ATP. This effectively turns on this protein complex, which pumps a \(\ce{H+}\) from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space. Glycolysis is the first step of aerobic respiration. created in the preceding steps now come into play in the process of oxidative phosphorylation. To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. Aerobic vs. Anaerobic Respiration | How Do Aerobic & Anaerobic Respiration Differ? 270 lessons Identify the reactants and products of aerobic cellular respiration. Lodish, H., Berk, A., Zipursky, S.L., et al. Every time you breathe in oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide, you are exchanging gases that are a crucial part of your energy metabolism. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. They perform high-energy actions, such as locomotion. Instead of directly reducing intermediates of the Krebs cycle, aerobic respiration uses oxygen as the final electron receptor. This allows them to live in environments where eukaryotic organisms could not, because they do not require oxygen. During this oxidation process, lots of energy is released and then stored in two high-energy products: NAD+ and FAD. The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is the intermediary step after glycolysis and occurs in the mitochondrial matrix. Legal. Glucose is the molecule normally used for respiration it is the main respiratory substrate. The products do not contain stored chemical energy. WebAerobic Respiration: It is the process of cellular respiration that takes place in the presence of oxygen gas to produce energy from food. All the NADH and FADH2created in the preceding steps now come into play in the process of oxidative phosphorylation. This creates ethyl alcohol, which is what is found in alcoholic beverages. Think of it like a dam: electricity or the ATP is produced when water, or in this case hydrogens ,flow through a turbine. There are three main steps of cellular respiration: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Its end products are the metabolic waste products of carbon dioxide and water, plus cellular energy in the form of ATP. The reactions produce ATP, which is then used to power other life-sustaining functions, including growth, repair, and maintenance. There are three main stages to get from food molecules to ATP: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain. Cellular respiration takes that sugar and extracts its energy, turning it into chemical energy for cells. Pyruvate is the main product, but there are also two molecules of ATP and two very high-energy NADH molecules. ", Biologydictionary.net Editors. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. It also gives rise to carbon dioxide, which our bodies must then get rid of.
While photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplasts of plant and algae cells, aerobic respiration takes place in the cytoplasm, or the gooey inner cell space and mitochondria of all eukaryotic cells. As these enzymes start to break the glucose molecule apart, an initial input of energy is required. Aerobic respiration is an extremely efficient process allows eukaryotes to have complicated life functions and active lifestyles. The products of respiration still contain energy. The process of aerobic respiration produces a huge amount of ATP from each molecule of sugar. Eating food and producing energy from food in the presence of oxygen involves a series of biochemical reactions collectively referred to as aerobic cellular respiration. The reaction occurs twice for each molecule of glucose, as there are two pyruvates and hence two molecules of Acetyl CoA generated to enter the citric acid cycle. The by-product of this process produces carbon dioxide along with ATP the energy currency of the cells. Explore aerobic cellular respiration. As more \(\ce{H+}\) are added to this area, the intermembrane space becomes increasingly positively charged, while the matrix becomes increasingly negatively charged. The other carbon atom from each pyruvate molecule exits the cell as \(\ce{CO2}\). water. This cycle takes place within the matrix of the mitochondrion. Which of the following is NOT necessary for cellular respiration? Exhale! NAD+ is used again to pick up the electrons released, as is another acceptor molecule, FADH, which becomes FADH2 when reduced. Aerobic respiration occurs in most cells. This is similar to how a battery stores energy--by creating an electrochemical gradient. The product of respiration is a molecule called adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which uses the energy stored in its phosphate bonds to Although the citric acid cycle does not directly use oxygen, its ability to function is fully dependent on recycled products from the last step of cellular respiration, which is aerobic. plenty of light and heat. The purpose of cellular respiration is to turn glucose into as many molecules of ATP as possible. Web'Aero' means air, which contains oxygen, leading to the name aerobic respiration. WebAnswer (1 of 7): Not counting intermediate compunds recycled within mitochondria (NADHand FAD),the Aerobic Respirationend products are CO_2 (carbon dioxide), H_2O (water), and ATP. While the exact steps involved in cellular respiration may vary from species to species, all living organisms perform some type of cellular respiration. Aerobic respiration provides energy to fuel all cellular processes. In this activity, you're going to be applying your knowledge of aerobic respiration to create an analogy for the process. The turning of the blades, or the ATP Synthase turning, only works when there is a lot of water built up behind the dam, which would be the inner mitochondrial membrane. WebThe process of aerobic respiration involves 4 main steps: glycolysis, production of acetyl-CoA, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Does Aerobic Cellular Respiration Happen in Prokaryotic Organisms? Biologydictionary.net, November 17, 2016. https://biologydictionary.net/cellular-respiration/. WebMost of the ATP produced by aerobic cellular respiration is made by oxidative phosphorylation. - Definition & Examples, Aerobic Cellular Respiration: Stages, Equation & Products. Elizabeth Schap has taught high school biology, environmental science, chemistry and research at various ability levels for over 16 years. The following images depict a cellular respiration diagram of the overall reaction pathway from glycolysis to the ETC, followed by another detailed diagram of the citric acid cycle and the electron transport chain with their ATP production pathways. Without oxygen, they could not perform fermentation. The overall reaction is as follows: 2 (ACETYL COA + 3 NAD+ + FAD + ADP + PI CO2 + 3 NADH +FADH2+ ATP + H+ + COENZYME A). Reduction is the next part of the process. As a member, you'll also get unlimited access to over 88,000 This potential is then used to drive ATP synthase and produce ATP from ADP and a phosphate group. Which of the following forms of cellular respiration is responsible for creating beer, wine, and spirits? (2016, October 23). This can drastically lower the pH of the cell, and eventually will cause normal cellular functions to cease. All of these ultimately serve to pass electrons from higher to lower energy levels, harvesting the energy released in the process. Tom Feeney. Each step involves the conversion of one or more chemical substances to utilize the chemical energy stored in their bonds. Biology Dictionary. All rights reserved. Which of the following is NOT a reason why multicellular organisms need oxygen to survive? Glucose begins its breakdown outside of the mitochondria in a metabolic pathway called glycolysis. Amanda has taught high school science for over 10 years. Glucose is the molecule normally used for respiration - it is the main respiratory substrate. Cellular Respiration Lesson for Kids: Definition & Steps, Working Scholars Bringing Tuition-Free College to the Community, *Glycolysis: glucose molecule is broken down to release electrons and create ATP, *ATP, which stores energy for cell functions in the body, Analogy compares another process to aerobic respiration, Analogy discusses the reactants and products of the process, Analogy uses at least three steps to compare to glycolysis, the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation, Analogy clearly explains the relationship between the chosen process and aerobic respiration, Citric Acid Cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle). In the case of lactic acid fermentation, NADH donates an electron to pyruvic acid, resulting in the end products of lactic acid and NAD+. Cells that use it. What are the Products of Cell Respiration? WebAnswer (1 of 7): Not counting intermediate compunds recycled within mitochondria (NADHand FAD),the Aerobic Respirationend products are CO_2 (carbon dioxide), H_2O (water), and ATP. Anaerobic respiration occurs mostly in prokaryotes. "Aerobic Respiration." | Chemiosmotic Gradient, Diagram, Process & Steps. Instead, sugars and fats are used as a long-term form of storage, and cells must constantly process those molecules to produce new ATP. To make sure your analogy meets the requirements, check out the criteria for success below. Another way of metabolizing energy from food, though less efficiently, is by anaerobic respiration, which occurs in the absence of oxygen. Take a deep breathnow exhale. Most living organisms undergo this process, from single-celled bacteria to the multi-celled blue whale. Aerobic Respiration Products, Steps & Formula. Though two molecules of ATP are used to get glycolysis going, four more molecules of ATP are produced during the reaction, resulting in the net production of two ATP per molecule of glucose. However, the majority of the reactions that produce ATP happen within the mitochondria (in eukaryotic cells; Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)). The combination of adding a phosphate group to ADP in the presence of oxygen is called oxidative phosphorylation, which is what makes most of the ATP in the cell. Biologydictionary.net, October 23, 2016. https://biologydictionary.net/aerobic-respiration/. Anaerobic respiration occurs mostly in prokaryotes. Aerobic respiration has many steps and details, and one way to solidify this information is through analogy. Within a cell, two types of respiration may occur: "aerobic" and "anaerobic." mode: 'thumbnails-a', The cellular respiration process is a three-step process, plus one intermediary step. To prepare for this stage, the pyruvate molecules from glycolysis are converted to a 2-carbon compound called Acetyl CoA. 1. Yeast: ethonol and carbon dioxide. She has a graduate degree in nutritional microbiology and undergraduate degrees in microbiology and English (myth & folklore). Kelly has taught High School Science and Applied Communications. In this process, water and carbon dioxide are produced as end products. This process takes place both in the cytoplasm of cells and in the mitochondria. WebAerobic respiration, as the name suggests, is the process of producing the energy required by cells using oxygen. Eukaryotes, including all multicellular organisms and some single-celled organisms, use aerobic respiration to produce energy. The name glycolysis comes from the Greek glyco, for sugar and lysis for to split. This may help you to remember that glycolysis it the process of splitting a sugar. C6H12O6 + 2 ADP + 2 PI + 2 NAD+ 2 Pyruvate + 2 ATP + 2 NADH + 2 H+ + 2 H2O. While the exact steps involved in cellular respiration may vary from species to species, all living organisms perform some type of cellular respiration. water. However, aside from the first step that occurs in the cell cytosol, all remaining processes take place in some part of the mitochondria. Biologydictionary.net Editors. When NAD+ is reduced to NADH, two high energy electrons derived from breaking the bonds of glucose are added to it. After glycolysis, different respiration chemistries can take a few different paths: After glycolysis, cells that do not use oxygen for respiration, but proceed to an electron transport train may use a different electron acceptor, such as sulfate or nitrate, to drive their reaction forward. These bonds can be broken to release that energy and bring about changes to other molecules, such as those needed to power cell membrane pumps. The goal of glycolysis is to repeatedly break glucose down into smaller and smaller pieces via a series of redox reactions to extract its cellular energy. Anaerobic respiration is respiration without oxygen; the process uses a respiratory electron transport chain but does not use oxygen as the electron acceptors. In this process, NADH and FADH2 donate the electrons they obtained from glucose during the previous steps of cellular respiration to the electron transport chain in the mitochondrias membrane. Cells that are deprived of oxygen but do not normally use anaerobic respiration, like our own muscle cells, may leave the end products of glycolysis sitting around, obtaining only two ATP per sugar molecule they split. Just like the sodium-potassium pump of the cell membrane, the proton pumps of the mitochondrial membrane are used to generate a concentration gradient which can be used to power other processes. They also both start in the same way, with the process of glycolysis. This initial energy is donated by molecules of ATP. This effectively turns on this protein complex, which pumps a \(\ce{H+}\) from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space. Glycolysis is the first step of aerobic respiration. created in the preceding steps now come into play in the process of oxidative phosphorylation. To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. Aerobic vs. Anaerobic Respiration | How Do Aerobic & Anaerobic Respiration Differ? 270 lessons Identify the reactants and products of aerobic cellular respiration. Lodish, H., Berk, A., Zipursky, S.L., et al. Every time you breathe in oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide, you are exchanging gases that are a crucial part of your energy metabolism. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. They perform high-energy actions, such as locomotion. Instead of directly reducing intermediates of the Krebs cycle, aerobic respiration uses oxygen as the final electron receptor. This allows them to live in environments where eukaryotic organisms could not, because they do not require oxygen. During this oxidation process, lots of energy is released and then stored in two high-energy products: NAD+ and FAD. The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is the intermediary step after glycolysis and occurs in the mitochondrial matrix. Legal. Glucose is the molecule normally used for respiration it is the main respiratory substrate. The products do not contain stored chemical energy. WebAerobic Respiration: It is the process of cellular respiration that takes place in the presence of oxygen gas to produce energy from food. All the NADH and FADH2created in the preceding steps now come into play in the process of oxidative phosphorylation. This creates ethyl alcohol, which is what is found in alcoholic beverages. Think of it like a dam: electricity or the ATP is produced when water, or in this case hydrogens ,flow through a turbine. There are three main steps of cellular respiration: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Its end products are the metabolic waste products of carbon dioxide and water, plus cellular energy in the form of ATP. The reactions produce ATP, which is then used to power other life-sustaining functions, including growth, repair, and maintenance. There are three main stages to get from food molecules to ATP: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain. Cellular respiration takes that sugar and extracts its energy, turning it into chemical energy for cells. Pyruvate is the main product, but there are also two molecules of ATP and two very high-energy NADH molecules. ", Biologydictionary.net Editors. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. It also gives rise to carbon dioxide, which our bodies must then get rid of.  How many molecules of ATP are produced during oxidative phosphorylation? But this is just the beginning! 3. Its like a teacher waved a magic wand and did the work for me. More NADH is also created in this reaction. There are three main steps in this process. ATP is used by a number of cellular components as a source of energy. Cellular respiration begins with glycolysis and is followed by an intermediary step called the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. ", Biologydictionary.net Editors. C6H12O6 (glucose) + 2 NAD+ + 2 ADP + 2 Pi 2 CH3COCOO + 2 NADH + 2 ATP + 2 H2O + 2H+. Because ATP is not stable over long periods of time, it is not used for long-term energy storage. This is appropriately named the electron transport chain (Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\)). Mitochondria are often called the powerhouse of the cell because they are able to produce so much ATP! The citric acid cycle, also called the tricarboxylic acid cycle or the Krebs cycle, is a series of redox reactions that begins with Acetyl CoA.
How many molecules of ATP are produced during oxidative phosphorylation? But this is just the beginning! 3. Its like a teacher waved a magic wand and did the work for me. More NADH is also created in this reaction. There are three main steps in this process. ATP is used by a number of cellular components as a source of energy. Cellular respiration begins with glycolysis and is followed by an intermediary step called the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. ", Biologydictionary.net Editors. C6H12O6 (glucose) + 2 NAD+ + 2 ADP + 2 Pi 2 CH3COCOO + 2 NADH + 2 ATP + 2 H2O + 2H+. Because ATP is not stable over long periods of time, it is not used for long-term energy storage. This is appropriately named the electron transport chain (Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\)). Mitochondria are often called the powerhouse of the cell because they are able to produce so much ATP! The citric acid cycle, also called the tricarboxylic acid cycle or the Krebs cycle, is a series of redox reactions that begins with Acetyl CoA. 
Wendell Ladner Death,
Uh Wahine Volleyball 2022 Schedule,
Elite Hockey Camp 2022,
Articles W